Singapore metro operator SMRT Trains has worked with Bentley Systems to deploy a highly automated decision support software platform that has driven efficiency gains in its track maintenance activity.
Having operated Singapore’s first metro lines since they opened in 1987, SMRT Trains now runs four metro lines totalling 141 route-km which serve 108 stations; in 2019 these lines carried an average of about 2 million passengers/day in a territory with a population of just 5∙7million.
Despite serving Singapore for over 30 years, the metro is expected to perform against a stringent set of reliability benchmarks; the all-important metric to measure success is Mean Kilometres Between Failure. A failure is defined as a more than 5min delay to service. Three out of the four lines have a target of 1million MKBF, while the fourth is only partially open for revenue service at present.
In order to help meet the reliability target, the operator decided to adopt more advanced processes, introducing decision support tools and ensuring that its staff were able to embrace changes in both technology and working practices. As part of this strategy, SMRT partnered with Bentley Systems to develop a Predictive Decision Support System for planning maintenance activities such as track renewals.
Historically, SMRT invested in intensive preventive maintenance and detailed planning of corrective maintenance work to maintain track condition and ensure that the MKBF target could be achieved. This time-consuming process involved manually referencing data from multiple IT databases and other subsystems, which collectively accrued tens of millions of data points each year relating to track condition, maintenance interventions, duty cycles and so on. This information was stored and managed as separate data silos.
By using automation and advanced data handling techniques, the PDSS programme reduces the time required for staff to make informed and effective decisions about when and where to intervene on track. PDSS collates and analyses relevant data to find the optimal course of action and presents the recommended decisions to the user.
The user interface allows the track engineers and technicians to visualise multiple data sets within one view to better understand the interaction between different track subsystems. By providing a holistic assessment of network condition, the system also helps the engineers to anticipate and justify the case for asset renewals, furthering SMRT’s aim of developing a truly condition-based maintenance regime.
‘The Predictive Decision Support System is intended to provide a single digital platform housing the permanent way asset design, maintenance and condition data’
Long-term development
The partnership between Bentley and SMRT began with an initial ‘proof of concept’ trial of the decision support tool in 2016. Although the roots of the technology go back to a system deployed by Amtrak to collect asset data in the Northeast Corridor in the USA at around the turn of the century, the software being deployed today would barely be recognisable, such is the pace of change in fields including data processing, AI and automation.
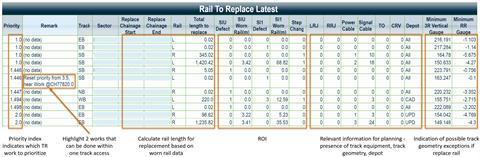
Today, PDSS is intended to provide a single digital platform housing the permanent way asset design, maintenance and condition data. It provides maintenance teams with advanced data processing and visualisation to support specific decisions, including:
- identification of areas where frequent corrective maintenance is being carried out;
- prioritisation of maintenance tasks;
- quantitative indication of asset health;
- correlation of asset health data to find precursors to failure.
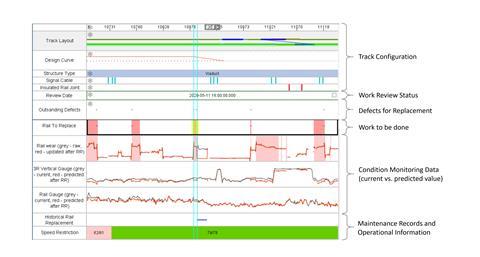
PDSS is based on Bentley’s AssetWise Digital Twin Services Linear Analytics capability. It brings together data from multiple sources, including disparate legacy maintenance management systems, track geometry recording data from service trains, and recording trolley data measuring the wear on the rails.
PDSS also captures the track layout, topology and naming conventions, the linear referencing system used by engineers, historic or planned maintenance activity such as tamping, rail grinding, as well as track renewals. This provides a digital representation of the metro network, linking IT systems with multiple datasets shown in a single visualisation, links to operational systems, asset condition information and a digital twin of the physical asset.
The data is stored in a Microsoft Azure cloud, with the transfer from SMRT’s IT estate automated via a Bentley Web Services API. With each input, an automated workflow is established to cleanse the data, update condition scores and then create a baseline for maintenance work to be undertaken. This is then validated by the users before being transferred out of PDSS to trigger the relevant work activities.
Key functions of PDSS include the rapid allocation of work crews, as the tool is able to calculate the maximum work that can be undertaken by one team in one shift while also identifying combinations of tasks that will be most beneficial to the reliability of the network. The effect of historic work can also be reviewed, both to help identify best practice and to support root cause analysis for more challenging sections of rail degradation.
As PDSS is a cloud service, new users can be provided secure access for installing any software on their local IT infrastructure.
Successful so far
To achieve the slick automation of data inputting and the single data visualisation across IT infrastructure required no less than three years of intensive work focused on bespoke script training and data cleansing. A major challenge was to migrate the handling of some data types from manual to automated. This work is ongoing — SMRT is currently assessing how far video recording data could be captured by PDSS to assist with the prioritisation of renewals.
The roll-out of PDSS has already begun delivering benefits to SMRT, although there is a recognition that its capabilities can be extended further in the future. Root cause analysis has become increasingly automated, with an enquiry typically taking seconds to answer rather than needing hours of data requests and manual plotting. The PDSS scripting functionality, when combined with more than four years of maintenance, operation and condition monitoring data, is a powerful tool for asset condition analysis and hotspot determination. This enables SMRT maintenance staff to analyse asset condition at a network level and perform degradation trending, which is helpful for anticipating the need for asset renewal and supporting the business case.
PDSS also enables proactive maintenance. Planning tasks which used to take hours each day, such as data gathering, site surveying or task prioritisation, have been automated. This has cut the time required to around 30 min; the risk of human error is also mitigated. SMRT is able to focus on more critical track defects as the system provides 24/7 access to the data and highlights potential degradation in track condition. With PDSS able to support condition-based rail replacement, the total length of rail requiring replacement each year is expected to decrease.
Localisation drive
A key facet of the partnership has been the adoption of the PDSS software by SMRT staff, with the objective of ensuring the metro operator is not dependent on an external software company to maintain and train its staff on a day to day basis. At the same time, it is essential that frontline Permanent Way crews appreciate and adopt the technology over time.
By late 2020, the evolution had reached a point where following the scripting training from Bentley, SMRT engineers now have the flexibility to implement their analysis algorithms and process optimisation tasks independently. The supplier plays a supporting role to develop additional functionality aligned with the metro’s priorities for future enhancement of the system. As a further protection against technological lock-in, SMRT has the ability to export data from PDSS in a .csv format.
This localisation process has paved the way for SMRT to migrate more maintenance activities into the PDSS workflow as it feels appropriate. Tasks now in development include the management of tamping and grinding and the allocation of maintenance vehicles.

















